Once considered exclusively as a weight-loss procedure for severely obese patients, there is more than 20 years of evidence supporting metabolic surgery as an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes, resulting in improvement or remission in the majority of cases.
Obesity is medically defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m² or more. It is a significant independent risk factor for developing the disease. Approximately 90% of people with type 2 diabetes are obese or overweight (BMI of at least 25).(21).
Randomized clinical trials show that metabolic surgery, especially gastric bypass, achieves results of complete remission or improvement of diabetes within two years in more than 90% of patients, in some cases at the time of hospital discharge and even before significant weight loss occurs. (22).
Studies show that metabolic surgery is superior to non-surgical treatment involving drugs. Intensive therapy and intervention in the style of producing long-term diabetes remission, with 25-50% more patients than surgery maintaining glycemic control without medication. (23) (24).
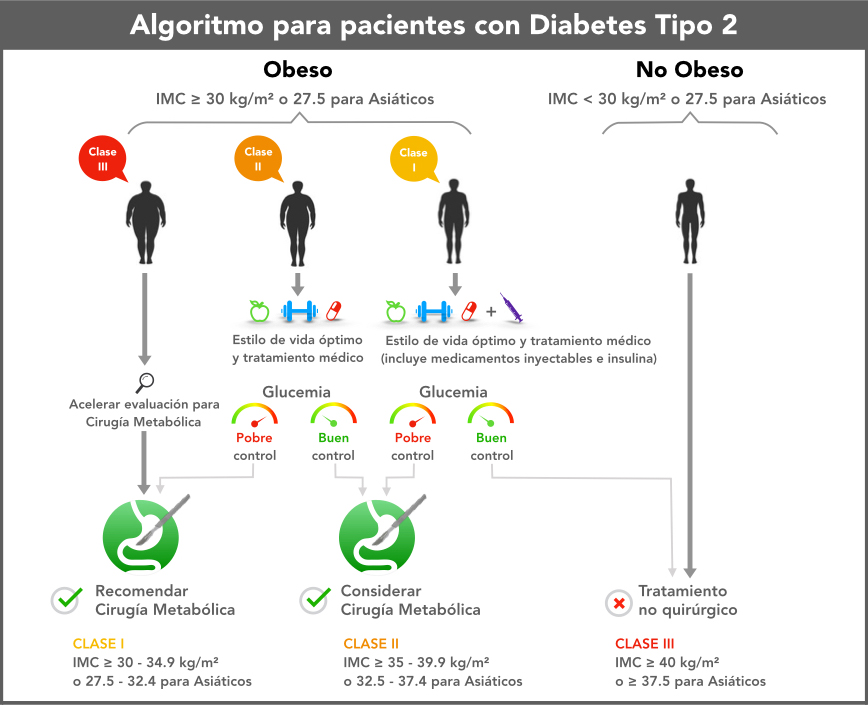
Global clinical guidelines approved by 45 professional medical societies include metabolic surgery as a treatment option for type 2 diabetes in patients with a BMI of 30 or more. (25).
Main Guidelines and Recommendations
2018: The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) Position statement on the role of bariatric surgery in class I obesity (BMI 30.0 to 34.9 kg/m2) states, “Particularly given the presence of high-quality data in patients with type 2 diabetes, bariatric and metabolic surgery should be strongly considered for patients with a BMI of 30 to 35 kg/m2 and type 2 diabetes.” The statement is supported by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and has been endorsed by the American Society of Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES). (26)
2018: ADA’s annually updated “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018” guidelines maintain an emphasis on metabolic surgery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, including the 2017 expansion of the indication for metabolic surgery to include patients with inadequately controlled diabetes who are mildly obese, with a body mass index as low as 30.
Surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes
Impact of Metabolic Surgery on Diabetes
Meta-analysis of more than 135,000 metabolic surgery patients (average BMI 47.9) In 621 studies (1990-2006) they found 86.6% of people with type 2 diabetes experienced improvement or remission, and overall excess weight loss (EWL) was 59.9% (American Journal of Medicine, 2009) (27)
Metabolic surgery versus medical therapy
Randomized clinical trials have shown that metabolic surgery is more effective than medical therapy and/or lifestyle interventions including drug therapy in producing diabetes remission, glycemic control, and weight loss. The five-year final results of the Surgical Treatment and Drug Efficiency Study (STAMPEDE) in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (mean BMI 37), showed that metabolic surgery plus intensive medical therapy treatments is more effective than intensive medicine alone in achieving and maintaining glycemic control, weight reduction, reduction of medication, and improvements in lipid levels. (NEJM, 2017) (28) (29) (30)
Diabetes remission rates at one, three, and five years with metabolic surgery were about 40% (gastric bypass 42%; sleeve gastrectomy 37%, 31% (gastric bypass 38%; sleeve gastrectomy 24%), and 26% (gastric bypass 29%; sleeve gastrectomy 23%), respectively compared with 12%, 5%, and 5% for medical therapy.
Long-term results with Metabolic Surgery
- Among patients with type 2 diabetes who underwent metabolic surgery, 24% experienced complete, long-term remission—five years or more—of their diabetes; 26% experienced partial remission; and 34% improved from baseline; the mean excess weight loss was 55% (Annals of Surgery, 2013). (31)
- Fifteen years after metabolic surgery, 30.4% of patients maintained diabetes remission, compared with 6.5% of control patients (JAMA, 2014) (32)
Reduction in diabetes-related mortality and health complications
- Metabolic surgery significantly decreases the likelihood of death, leads to lasting improvements in important cardiovascular risk factors, and reduces the risk of developing microvascular complications.
- Patients with severe obesity who had gastric bypass surgery reduced their risk of mortality from type II diabetes by 92% for up to seven years (NEJM, 2007) (33)
- Gastric bypass in patients with type 2 diabetes was associated with a 58% reduction in the relative risk of death from any cause five years after surgery (The Lancet, 2015) (34)
- Risk of death from myocardial infarction (heart attack) was reduced by almost 60%
- Risk of non-fatal or fatal myocardial infarction reduced by 49%
- At 12 years, patients with type 2 diabetes who had gastric bypass saw lower rates of hypertension (16% vs. 47%) and dyslipidemia compared to those who did not undergo surgery (NEJM, 2017) (35)
- Meta-analysis of 17,532 patients in 1,559 studies demonstrates metabolic surgery was superior to medical treatment alone in patients with obesity for the prevention of microvascular complications of diabetes (OR: 0.16 vs. 0.42), including nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy (British Journal of Surgery, 2018) (36)
- For patients with diabetes and severe obesity who had metabolic surgery, the five-year risk of microvascular complications was less than half that of patients receiving medical treatment 16.9% vs. 34.7%, respectively (Annals of Internal Medicine, 2018) (37)
The safety of metabolic surgery has improved significantly over the past two decades, with continued refinement of minimally invasive approaches (laparoscopic surgery), improved training and accreditation, and the involvement of multidisciplinary teams. The surgeon's experience and skill are essential factors determining the outcome of the surgery.
Metabolic surgery in patients with low BMI (Body Mass Index)
- Systematic review of more than 50 studies demonstrates that metabolic surgery in patients with mild to moderate obesity (BMI 30 to 35) produced greater glycemic control (range, 0.9 to 1.43 point improvements in blood sugar levels) and weight loss (range, 14.4 to 24 kg) after 12 months to two years compared with nonsurgical treatments (JAMA, 2013) (38)
- Diabetes remission was achieved in 931 TP3T gastric bypass and 471 TP3T sleeve gastrectomy patients with a BMI of 24 to 30 one year after surgery (Archives of Surgery, 2011) (39)
- Five-year data in patients with a BMI less than 35 shows that after metabolic surgery, 36% maintained complete remission of diabetes and 28% maintained partial remission compared to 1,2% and 1,6% of patients treated with medical therapy alone (Archives of Surgery, 2015) (40)